While edge computing has many benefits, it cannot replace cloud computing. Its capacity is limited by resource constraints, and not everything can be run at the edge. Rather, it complements cloud computing by radiating outward to the “ends” of a network. Here are some examples of where edge computing may be useful.
Edge computing reduces network latency
Edge computing can reduce network latency by reducing the number of hops between the device and the server. This reduces the cost of transmission while improving response time for end users. Edge computing can be used for a number of reasons, including indoor farming, where the data is collected and analyzed locally.
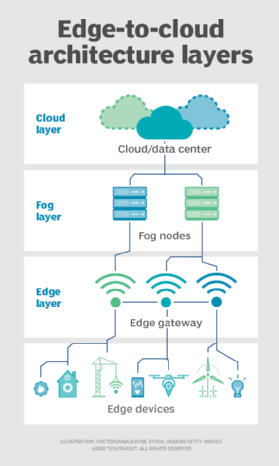
The growing number of internet-connected devices has created a need for devices at the edge of the network. However, these devices don’t have the computing power or storage needed to process large amounts of data efficiently. For these reasons, companies are developing new edge devices that can process data at the edge of the network. Those devices are referred to as edge nodes, and they must be compact and powerful.
In the world of big data, businesses face new challenges, and one of those challenges is latency. They must move data closer to their end users and process it faster, enabling faster action. By using edge computing, companies can eliminate these problems and keep their data closer to their end users. Moreover, companies can determine which information needs to be immediately accessible, and how much can be stored for later use.
Edge computing technologies are being developed for healthcare and are expected to continue to grow in the next few years. They will change how we deliver health care in the future. For example, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning can transform the speed and location of clinical care. One recent example is a platform incorporating facial recognition technology and automation. Using the platform, patients can register for clinical visits using their smartphones and receive messages from their healthcare providers prior to their exams.
Edge computing reduces network latency by reducing the amount of round-trips that are necessary to send data. It also allows for real-time, automated decision-making.
Are you interested to buy discounted Nvidia products? Contact IoT Worlds today.
It reduces the need for cloud computing
Edge computing is a type of server that can operate offline, which makes it ideal for a variety of situations. Its benefits include reducing latency, producing faster responses, and helping prevent operational failures. It is also helpful in locations where there is a limited Internet connection, such as oil fields. Additionally, edge computing can help protect against cybersecurity and compliance issues. These issues are becoming increasingly important as governments worry about companies’ use of consumer data, as outlined by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which took effect in the EU in 2018.
Edge computing is also beneficial for healthcare facilities. For instance, it can be used to predict the spread of a deadly disease by analyzing data from nearby medical devices. The ability to process data at the edge level can help hospitals and healthcare organizations improve the efficiency of data processing. The cost of sending data from remote sites across a central server is high and data transmission can take seconds. In addition, edge computing supports local application availability even during network outages.
Other edge computing applications include autonomous vehicles, which will generate massive amounts of data and will require real-time processing. This is one of the fastest-growing potential uses for edge computing. The development of autonomous vehicles will also lead to increased investment in related technologies, such as computer vision systems and 5G network infrastructure.
Edge computing also reduces the need for cloud computing by allowing data to be processed closer to where it is generated. By using micro data centers, edge computing can decrease data transfer from the data source to the cloud. According to IDC, the footprint of edge computing infrastructures is under 100 square feet.
It improves reliability
One of the biggest concerns of organizations using edge computing is the reliability of data transmission. While edge computing can help improve this, it is important to have a back-up plan in case something goes wrong. If you are considering edge computing for your organization, here are some of the things to keep in mind.
First, edge computing helps address three major limitations in network infrastructure: latency, scalability, and data volume. In healthcare, remote monitoring of patients is common practice. This allows health professionals and patients to get real-time data, such as vital signs. However, this also presents a significant challenge – processing large amounts of healthcare data. Furthermore, healthcare solutions cannot tolerate high latency when transmitting data, which is why edge computing can be an excellent solution.
Edge computing also helps reduce latency by bringing heavy traffic closer to the user. This reduces latency and increases user experience. In addition, it can replace data centers and reduce costs. In some cases, edge computing solutions can completely replace the need for data centers. This technology also provides high-performance processing capabilities and low-latency connectivity.
Another benefit of edge computing is that disruptions at the edge devices won’t affect the entire cloud implementation. In contrast, disruptions at a cloud data center can impact many users. Power outages or DDoS attacks would affect everyone on the entire network, while a disruption to an edge device would only impact local applications.
Are you interested to buy discounted Nvidia products? Contact IoT Worlds today.
It is not a stand-alone solution
The phrase “Edge computing” originally described a technical solution that was developed in the 1990s to solve the problem of rapid growth of the internet and web. The problem occurred when the ever-increasing volume of website traffic exceeded the capacity of commercially available servers. The solution involved reducing latency and increasing speed.
Edge computing works by placing processing and storage closer to the source of data. The idea is that this approach will reduce latency and save bandwidth. However, edge computing is not a stand-alone solution and must be integrated into a larger network infrastructure. The challenges edge computing solutions address are performance, autonomy, privacy, and economics.
In order to reap the benefits of edge computing, companies must ensure their devices are robust and resilient to the elements of a harsh edge environment. They also should partner with a company with experience in the field. A partner such as IoT Worlds can help clients with planning and building out edge solutions. Contact us today!
Edge computing can help businesses save on bandwidth costs by performing processing closer to the data source. It can help process data from sensors. For example, railway stations can place a small amount of computing and storage at the edge of the network. The results of edge computing can then be sent back to a data center for further processing and broader analytics.
Edge computing can streamline the amount of data a business can process at a time and provide convenience to customers. It also enables businesses to access detailed data and insight at a much faster rate. With this kind of data at their fingertips, businesses are better able to predict future demand and adapt to it better. This approach will enable businesses to reduce their costs while eliminating the complexity and inefficiencies of traditional IT solutions.


