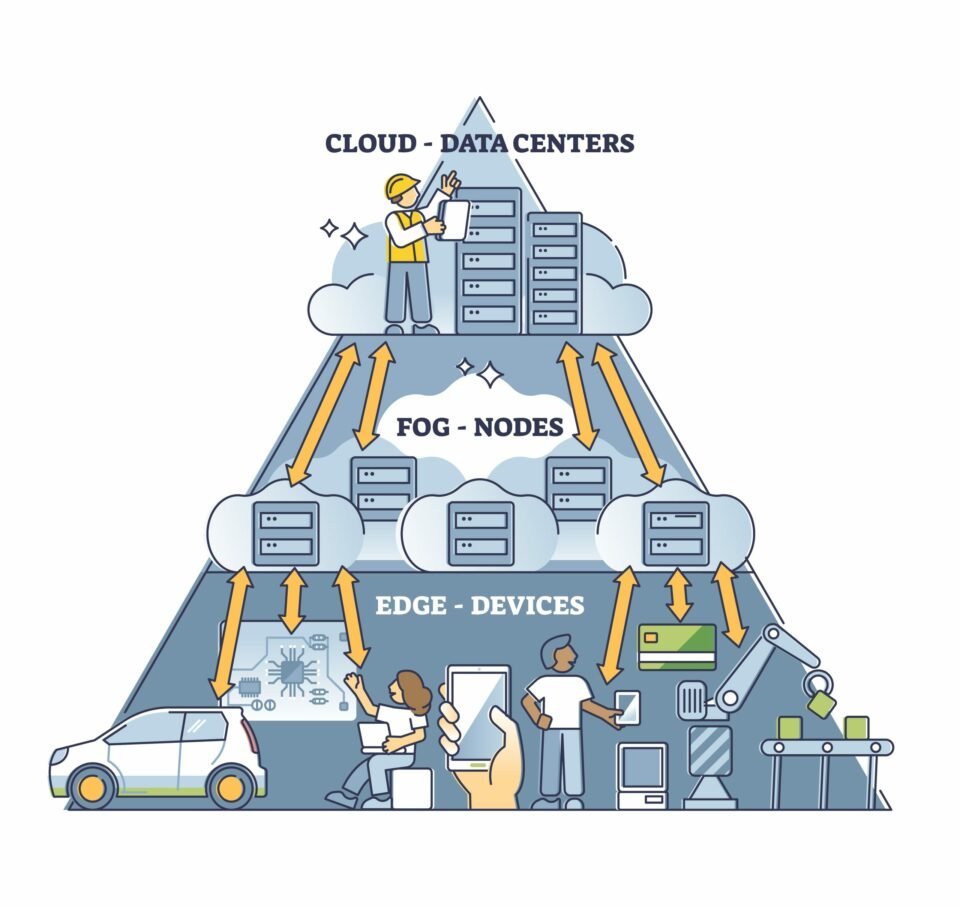
There are several situations where edge computing can be beneficial. Some of the benefits of this technology include: reduced energy consumption, reduced network latency, reduced data redundancy, and improved compliance with local regulations. In addition, edge computing is an excellent way to provide services to those without a computer or an internet connection.
Reduces energy consumption
Edge computing moves processing power from the cloud to the end user. This is especially beneficial for video streaming services. According to Google, mobile networks consumed a large portion of the energy used by YouTube in 2016. By hosting content closer to the end user, it mitigates the need for mobile networks to carry traffic over the internet. This frees up bandwidth for other applications.
While large data centres can aggregate the storage and compute requirements of thousands of users, they may not be optimally configured to optimise energy consumption. In addition, cloud data centres typically operate 24 hours a day even when they aren’t in use. On the other hand, edge data centres may need to deal with variation in utilisation and make resources dormant when not in use. As a result, orchestration and proper design must be built into the design of distributed data centres.
Edge computing is becoming increasingly important to organizations that are seeking to reduce energy consumption and waste. It allows companies to run more efficiently, while maintaining a sustainable approach to operations. Edge computing solutions are also helpful for organizations looking to implement AI-driven sustainability applications. With this technology, businesses can improve their operations by adopting smart data and machine learning models to reduce their energy use.
Another advantage of edge computing is that it can reuse existing hardware and reduce the need to invest in new hardware. This not only saves money but also reduces carbon emissions. By leveraging existing hardware, companies can avoid purchasing expensive new infrastructure and cutting the need for new IT equipment. It can also increase the durability of industrial systems and help them run offline.
In addition to reducing bandwidth and latency, edge computing can reduce overall energy consumption and increase efficiency. Research indicates that organizations with a focus on sustainability can also see an increase in customer loyalty and revenue. This is because the increased use of green technologies by companies helps them reduce their environmental footprint.
Using edge computing can also help cut down on waste. For instance, when users need to access video on-demand services, they need less data to traverse the internet. This reduces energy usage because fewer data must travel long distances. Further, by keeping data close to the end users, the costs associated with data leaks can be reduced, while ensuring the security of personal data.
Reduces data redundancy
Edge computing is a technology that can help organizations cut down on their data redundancy by deploying data servers closer to where users are. For example, a bus can be equipped with a computer that helps the driver find the most efficient routes. A delivery truck can be equipped with the same technology. Edge computing can help companies keep websites up and running smoothly and reliably by using data servers located close to the location of the user.
Data redundancy is a problem for organizations for several reasons. First of all, it wastes server storage space by storing the same data in different databases. The less storage space a company has, the slower data retrieval time will be, which can negatively impact business performance. In addition, storing the same data in multiple locations can result in data corruption. This can lead to corrupt reports and analytics.
While transferring data to the cloud can be time-consuming, it is essential to minimize latency when it comes to critical data. Edge computing technology can solve this problem by bringing analytics capabilities closer to the machine and eliminating the middle man. This can reduce the cost of data transfer and improve asset performance.
While data redundancy has its benefits, it should only be implemented when it’s purposefully created. Redundant data is data that is stored in two or more locations to ensure that it is still available in the event of a disaster. This can occur in a computer system, on a local device, or in a cloud storage system. It can also be an important part of a business disaster recovery plan.
In smart agriculture IoT applications, edge assisted data collection can reduce the amount of redundant data in the system, thereby decreasing latency and energy consumption. It also improves data collection by balancing the amount of data with main event information. For instance, in a software-defined wireless sensor network, key features data types are extracted from an historical data set and used for collection data.
Reduces network latency
Edge computing is a new approach to data processing that reduces network latency while increasing network performance. It works by relocating data processing from the central data center to a local network. The result is lower latency, improved network performance, and lower data traffic. Edge computing solutions are now being offered by all the major telecom operators in India in partnership with equipment vendors. Bharti Airtel, for example, has partnered with IBM to deploy this distributed computing platform in large enterprises across many industries.
Edge computing uses hardware and software close to the data source, reducing the overall network latency. By doing so, data is processed closer to where it is needed, resulting in better security, more bandwidth, and improved network stability. In some cases, edge computing can eliminate the need for a data center altogether, since processing occurs locally.
Edge computing is closely related to cloud and fog computing, but they are not the same. While both technologies focus on distributed computing, the main difference between them lies in the location of the computing device. Edge computing is physically located near the device, while cloud and fog computing are cloud-based.
Edge computing is particularly useful in the manufacturing industry. The technology allows for processing data closer to the location where it was generated, reducing network latency and enabling manufacturers to make better predictions about processes on the factory floor. This also improves predictive maintenance capabilities. In addition to reducing network latency, edge computing is used in a wide range of other applications.
It has the potential to impact both the wireless industry and society. Wireless networks are vital for the delivery of demanding applications. They provide data and control between cloud services and mobile devices. However, they are also limited in bandwidth and latency. Further, they are prone to congestion. As more mobile devices are connected, this congestion causes network latency, which results in higher response times for mobile users.
Edge computing helps reduce network latency and reduces network costs. It can also improve security by eliminating the distance between data collection and computation. Edge computing also reduces the security concerns associated with sending sensitive data across borders.
Improves compliance with local regulations
Edge computing is a technology that puts servers and storage where the data is – in a local location. This means that only a portion of the gear must be sent to the main data center for processing. Typically, this gear is placed in a hardened or shielded enclosure. Often, edge computing processing involves business intelligence and normalization of data streams. Once this processing has been completed, the results are sent back to the main data center.
Edge computing can also improve compliance with privacy regulations. Many countries are implementing data retention laws and regulations, which affect companies that store and process personal information. In the EU, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has strict requirements that all organizations collecting and using data of EU citizens must comply with. Edge computing can help organizations meet GDPR requirements and avoid data leaks. Smart cities can also make use of edge computing to analyze surveillance video locally.
Edge computing also provides cost savings. By storing sensitive data in the same location, edge computing can help companies reduce network bandwidth and security expenses. Edge computing also helps organizations adhere to local regulations and implement “just-right” physical and digital security policies. However, the local IT staff at edge locations can be scarce, making it challenging to maintain security and compliance standards.
Contact us for any activity related to Edge Computing!
Edge computing makes it easier for companies to comply with regulations in more than one jurisdiction. With the proliferation of mobile computing, enterprises have become more exposed to regulatory issues. Company devices are now outside the enterprise’s protected firewall perimeter. However, data that is processed locally is still protected by on-premise enterprise security. Edge computing also helps companies overcome issues of data sovereignty and privacy regulations.
Edge computing is especially useful when bandwidth is limited or unreliable. For example, edge computing can be used on oil rigs, ships at sea, and even on remote farms and villages. By reducing bandwidth, edge computing can significantly reduce data that must be transmitted.