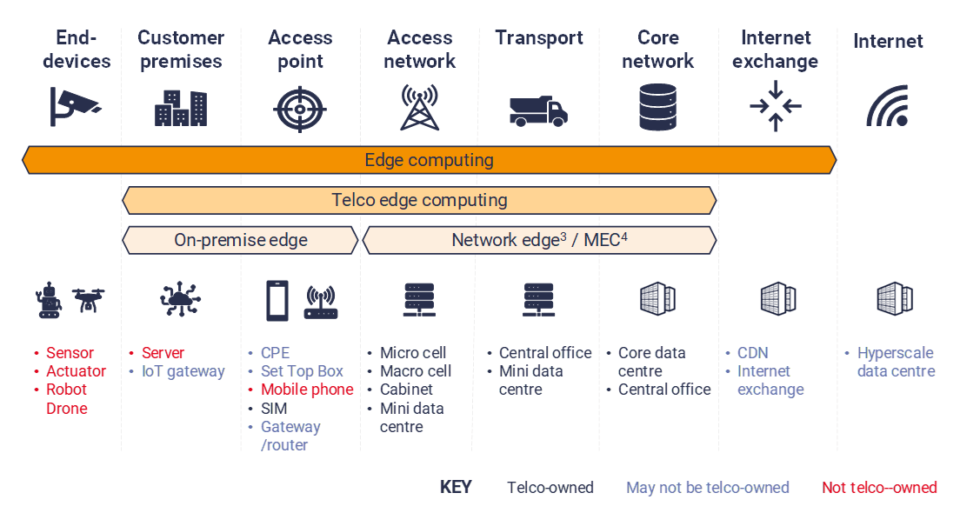
Edge computing covers devices that have connectivity but do not necessarily need high-speed connectivity. Examples include retail kiosks, cameras, factory sensors, connected cars and drones, smart parking meters, and streetlamps. Typically, latency expectations for edge computing are below 5 milliseconds. Regardless of the device, edge computing is a powerful technology for many different applications.
Mobile
Edge computing is a computing paradigm that leverages the power of mobile devices. By distributing computing tasks across multiple devices, it allows for better utilization of resources. Its utility function assigns a priority value to offloading requests based on the computing demands and required resources. As such, it minimizes the cost of developing mobile applications and ecosystems.
To enable edge computing on mobile devices, cellular networks can augment their existing network equipment. These devices can be outfitted with specialized hardware appliances that allow for stateful communications. These appliances can be complemented by a software library that runs on a general purpose server system. The software library can also be used on a mobile device.
The use of virtualization and container technology is a key part of edge computing. Both technologies help to separate computing resources while preserving the integrity of data. However, these technologies can cause negative impact on device performance. As an alternative, edge OS is packaged as a single binary that includes container runtime and important host utilities.
One example of a hybrid architecture for edge computing is the deployment of Docker containers. It can facilitate fast service deployment and disassembly, which is essential for edge computing. Another approach, developed by Petrolo et al., is to deploy lightweight virtualization technology on the IoT gateway. This technology helps to provide a scalable IoT gateway. It also enables dynamic services and improves the gateway’s performance.
The ESIRS server 75 receives the mobility event signal and transmits it to the destination EdgeApp proxy. The ESIRS server then triggers state reconstruction at the destination EdgeApp proxy. It also transfers EdgeApp-specific logged state data.
Fixed access
EdgeC is an emerging technology that has the potential to transform wireless industry and society. Today, wireless networks provide data and control to mobile devices, but their capacity is limited and they suffer from high latency due to increased device density. This can negatively impact the delivery of high-demand applications, especially when a large number of devices are connected to a single network.
In addition to extending the capabilities of the network, edge computing can help operators rethink their backhaul business models. Rather than sending data back to the cloud for analysis, data can be filtered, rationalised and stored locally. This way, only the data that is needed can be sent to the centralised cloud. This can help operators reduce costs and improve customer experience. It also provides an incentive for application developers to utilize edge computing sites.
The advantages of edge computing include lower latency, increased bandwidth, and real-time applications. According to Gartner, 80 percent of enterprises will shutter their traditional data centers by 2025 as their business models shift to incorporate edge data centers. As the adoption of 5G continues, the multi-access edge computing market is predicted to reach $13.5 billion by 2024. Ultimately, this technology will bring the power of the cloud closer to the customer.
Edge computing is increasingly used for enterprise organizations, such as large public venues. The content delivered to the onsite consumers is stored, processed, and delivered locally without backhauling through the centralized core network. Small cell networks have become a popular option for enterprises as well, and the ETSI is studying its potential. OpenStack, meanwhile, offers an exploration of edge computing.
Cloud
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that moves computation and storage closer to the data source. It is designed to improve response time and reduce bandwidth consumption. While this is a general architecture, there are some details that need to be understood before you begin implementing it. Specifically, edge computing is location and topology sensitive.
As the term suggests, edge computing runs on lower-powered hardware. It shares its core with cloud computing and is based on community-developed software. In contrast, cloud computing uses larger and more powerful servers. However, the cost of global edge clouds is prohibitive for most non-hyperscale providers.
While cloud computing allows for large amounts of data, it has many drawbacks. For example, data is transferred across large distances, which can lead to network overload. In addition, cloud computing cannot handle the sensitive nature of some data. Moreover, data transmission requires time and energy. Thus, edge computing is better suited for applications that require real-time results. However, both cloud and edge computing remain relevant. The two technologies will continue to work together to deliver real-time solutions and data analytics for organizations.
While cloud computing is an emerging technology, it is also a crucial component of IoT deployments. With more IoT devices becoming increasingly connected, the need for a cloud infrastructure is growing. In the meantime, edge computing solutions help users get their data in real time without the need to wait for large data centers.
Edge computing is an approach to distributed computing that puts computing resources, data, and intelligence closer to users. By doing so, businesses can reduce costs and build more performant IT ecosystems. However, this approach requires computers to communicate with distant servers, and the resulting latency is problematic for real-time applications that require large amounts of RAM.
Are you ready to develop your Edge Computing solutions with IoT Worlds? Contact us!
Device
Edge computing is a type of computing where data processing takes place in a local environment. Typically, this is a wired or wireless LAN. Sometimes it involves a private data center. It can also use the internet or WAN to communicate. This type of computing can help reduce latency and reduce bandwidth usage.
Some applications of edge computing are in the healthcare field. It can help monitor medical equipment and prevent serious health issues by transmitting data directly to monitoring machines. For instance, an optimal video camera model can send live streams only when motion is detected, rather than continuously sending traffic to the cloud for processing. This technique is known as “tripwire detection” and makes use of edge computing at the sensor level.
There are several types of edge computing, and each has its own advantages. For example, premises edge computing uses dedicated compute and storage devices to provide network routing, security, and data filtering. It can also host applications. Premises edge devices can come in different shapes and sizes. Their advantages include being closer to customers, a shorter direct path to the edge cloud, and a low latency.
Another example of edge computing is in the field of smart homes. These devices are typically located in different locations and have dedicated functions. They can be connected to public or private networks. They can also be autonomous. As a result, edge computing can enable seamless functioning of these devices. These devices are equipped with sensors that collect data in real time.
There are several types of edge computing environments, and each one has advantages and disadvantages. Nevertheless, mobile edge is one of the most versatile and scalable edge computing environments. It is a distributed computing environment that distributes computing power between mobile and non-fixed IoT devices. This type of computing is a perfect fit for businesses that travel a lot or rely on mobile devices.
Sensor
Sensor-based edge computing uses sensors to provide data and intelligence. These sensors are battery-powered, so they need to be able to operate for many years without having to be recharged. Ideally, they should also be able to be powered by energy harvesting. This reduces the amount of compute power that the sensor needs and reduces the power usage of the system.
Sensor-based edge computing is used to improve network performance. By placing compute power closer to data sources, latency can be reduced and the data is processed locally. This helps avoid wasting bandwidth that is normally sent to a data center. In the case of video analytics, for example, the videos from hazardous locations can be processed locally to provide real-time information to operators.
A key advantage of this approach is that it offers better data sovereignty and security. The handling of data by multiple devices can cause security concerns, and the resulting edge processing requires careful analysis of security vulnerabilities and mitigation techniques. Sensors collect and transmit data by emitting electrical signals when they detect a change. After signal processing, the data can be converted into knowledge, such as a location’s temperature. Sensors also typically have additional circuitry, called subsystems.
Sensor-based edge computing enables companies to use analytics and machine learning at the edge. This enables businesses to make better decisions and improve the quality of their products. Industrial edge computing is already assisting in improving retail inventory accuracy and supply chains, as well as improving product development and customer experience. Retailers can use sensor-based edge computing to understand customer behavior in real-time.
Sensor-based edge computing uses artificial intelligence and machine learning. It allows for faster, more precise, and more energy-efficient computing. The concept of edge computing is a great leap forward in computing. It will redefine the direction of science and technology. However, it is important to note that the technology still has a number of challenges. Some of these include energy efficiency and privacy issues.
Are you ready to develop your Edge Computing solutions with IoT Worlds? Contact us!